



When you have successfully completed this section, you will have mastered the following:
Since the performance of vehicle wiring can be compromised by a wide variety of causes, it's vital that precautions be taken against as many of these circumstances as is practical. Some of these basics are included in the following section.
Wire Control & Protection
Tape
Tape should not generally be used alone for securing wire bundles, especially PVC plastic (polyvinylchloride), “electrical" tape. This should only be used to hold bundles of wires together within coverings such as looms and convoluted tubing. Some specialty tapes (such as glass fiber tapes) may be used where increased resistance to heat and chemicals are required. When using tape on the wiring of a truck, check the manufacturer's specifications for information on when to use.
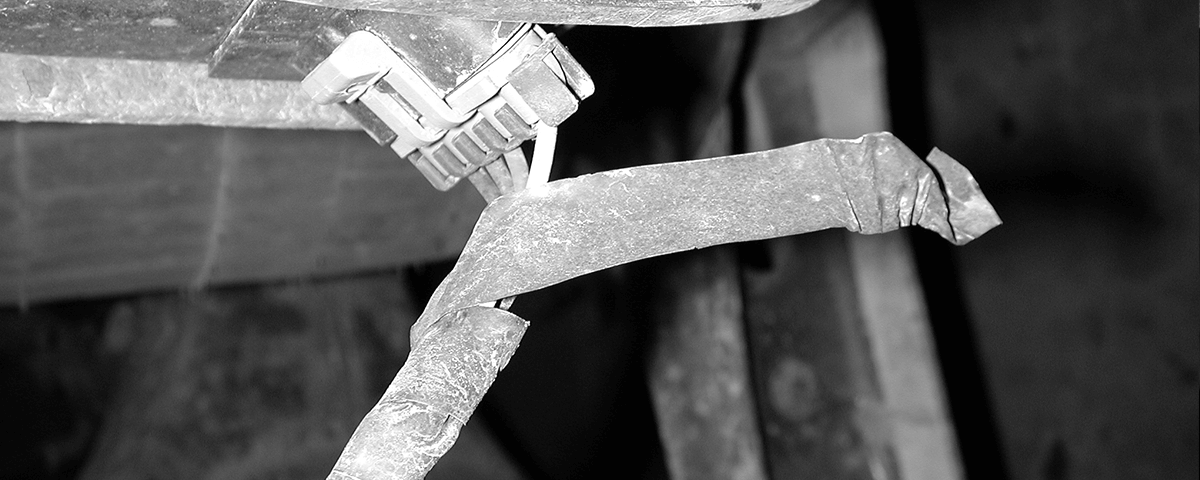
Standard electrical tape doesn’t hold up well under road conditions. It has a a tendency to lose its grip and come loose.
Heat Shrink Tubing
A good way to protect wiring installations is to use heat shrink tubing. Heat shrink tubing contracts under application of heat by a ratio of as much as four to one. It is designed to cover and seal connections against moisture, dust, grit, chemicals, corrosive materials and abrasion.
Heat shrink tubing is available in PVC, polyolefin, silicone and fluoropolymers. It comes in single wall or a dual wall version, which contains a layer of encapsulant that flows under heat to fill irregularities.
Some dual wall comes with a special hot melt adhesive.
This stands up to underhood temperatures as it forms a barrier against engine fluids, moisture, contaminants, corrosives and water wicking.
On a typical splice, a 2"-3" section of tubing is placed on the area to be covered. Heat is applied at the center until the tubing has contracted around the splice. Then the heat source is moved left and right until the entire section of tubing is snugly fitted around the wires.
Dual wall tubing is used to seal areas that are likely to be exposed to significant amounts of moisture or road splash. It can also serve as a strain relief where a wire joins a bundle.
Heat-Shrinkable Connectors
Even for simple splice connections, it's important to make the splice as water-tight as possible. To facilitate this, products are available that will make your job easier. Heat-shrinkable connectors protect splices from moisture while providing strain relief for the connection. They also protect against vibration, while completely insulating and protecting the electrical connection. Grote makes a heat-
shrinkable connector that has an adhesive lining to provide more reliable protection than conventional splices.
A high-quality heat-shrinkable connector also provides resistance to most vehicle related solvents including diesel fuel, antifreeze and brake fluid.
Heat Shrinkable Solder-Splice Connectors
For the ultimate spice connection, Grote makes a heat shrinkable connector that already contains the right amount of solder for a perfect splice. They're not only easy-to-use, but the integral solder helps to ensure that your spice won't come apart from vibration. The solder melts at 145° C (293° F). Maximum operating temperature for these connectors is 125° C (257° F). Solder-splice connectors are UL and CL recognized.
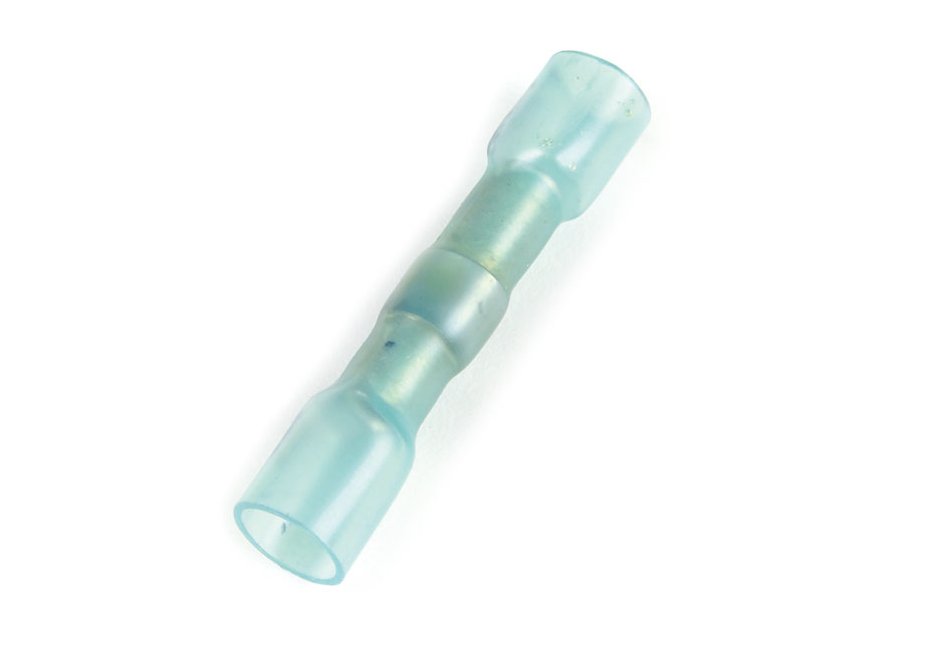

Heat shrinkable butt connector
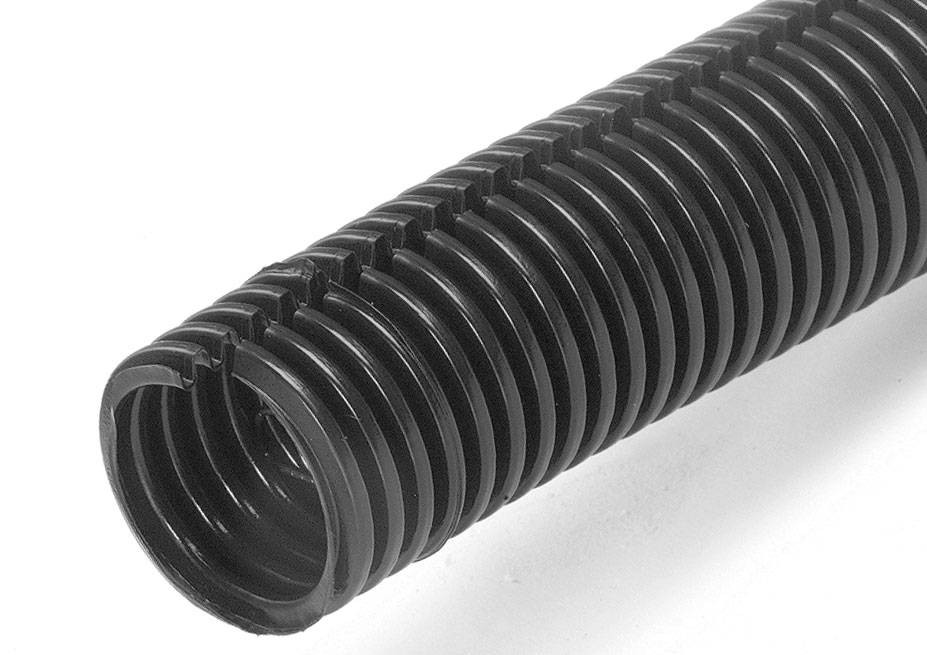

Products such as convoluted tubing will protect and neatly organize bundles of wire.
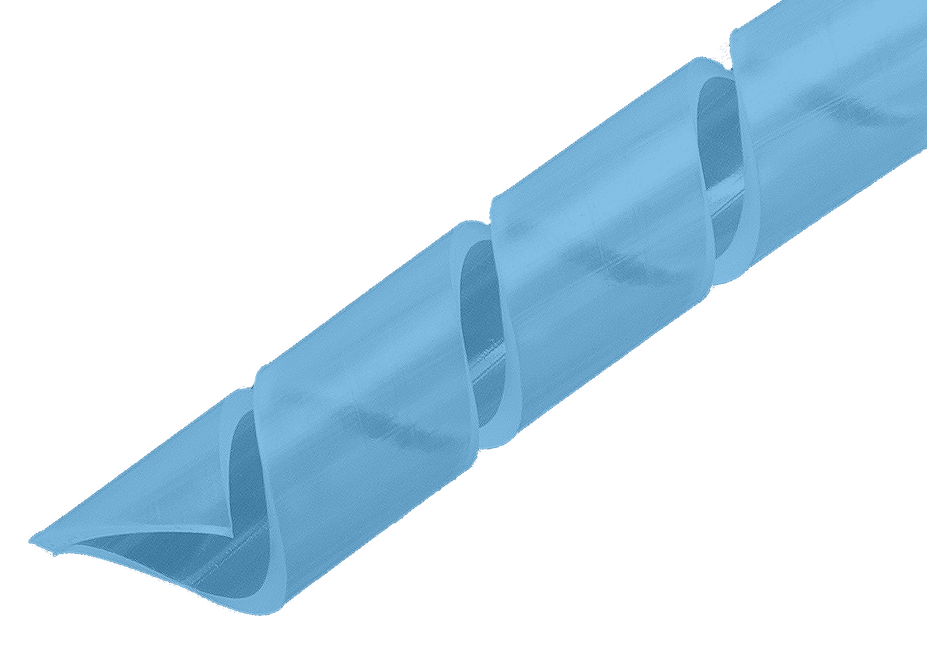
Spiral Wrap
Other Tubing Products
Another way to organize and protect wiring is with convoluted tubing. This product is designed to protect wires from detrimental environmental factors, while offering easy access to them. The material used is typically PVC, polypropylene, polyamide or other materials designed for special environments (such as extreme heat conditions).
This tubing is typically available from 1/2" to 2" in diameter and in slit and non-slit varieties. The slit version makes installation and later service easy and efficiently.
The slit variety should be secured approximately every 12 inches to keep the tubing closed and the wires contained.
Wiring should be secured wherever it exits the tubing to guard against abrasion from the edge of the tubing. The size tubing selected should allow the enclosed wire to fill approximately 80 % of its diameter.
Another product for controlling and protecting wiring is fiber loom. It protects against moisture with an asphalt compound and is non-metallic. Plastic loom is also available.
Spiral wrap allows easy lead out of wires because of the construction, which leaves a continuous slot the length of the tube. It has a built-in memory that allows it to stretch to accommodate a wire, then to regain its original size.
Boots/Covers
An alternate approach to protection is to use specially made rubber or plastic coverings, also referred to as boots. They are designed for attachment to the back of connectors, protecting them from water splash while offering a degree of strain relief.
Wire Support
An important factor in both installation and repair of wiring systems is to provide a series of secure attachment points along the installation route that keep wires in their proper locations. Proper support also helps protect them from vibration as well as keeping them out of the way of road debris that may be thrown up.
Secured wiring is less prone to snagging, tensile loading from snow and ice and contact with moving parts. Support points should be located every 12" to 18".
One of the most popular means of support is a clamp. Clamps come in a range of styles and sizes from ⁄" to 2" in diameter, and are made from lightweight nylon that is very resistant to corrosion and rust. However, nylon clamps may prove to be less durable than metal, especially where there are a large number of wires to be secured together. They are well suited for locations such as truck cabs and certain chassis areas.
For optimal performance of plastic clamps, the weight of the wire bundle must be reasonably low, the potential for impact, vibration and road shock moderate, and the heat environment less than 100ºC. Some plastics may turn brittle with constant exposure to high temperatures.
Metal clamps resemble the nylon variety in shape and also come in a similar variety of sizes. Some varieties of metal clamps are coated with a layer of neoprene rubber that cushions the wires from contact with the edges of the clamp body. This rubber coating also provides a layer of insulation and resists corrosion.
Wire ties are another approach to securing wires. They are used over short routes when the number of wires is modest and the bundle is supported by the mounting surface.
Ties come in a variety of sizes and types ranging from miniature to heavy duty and from black and white to colors (making it easy to color code bundles). A particularly useful type is the “Mounting Tie", which has a hole drilled in the body of the tie to allow a screw to secure the bundle in place on a chassis component.
Acceptable fasteners include rivets or correctly sized threaded fasteners, such as screws and bolts. Certain types of plastic fasteners such as Christmas tree barbed styles and snap-in studs are also acceptable. Plastics are used in cabs and in certain chassis areas.
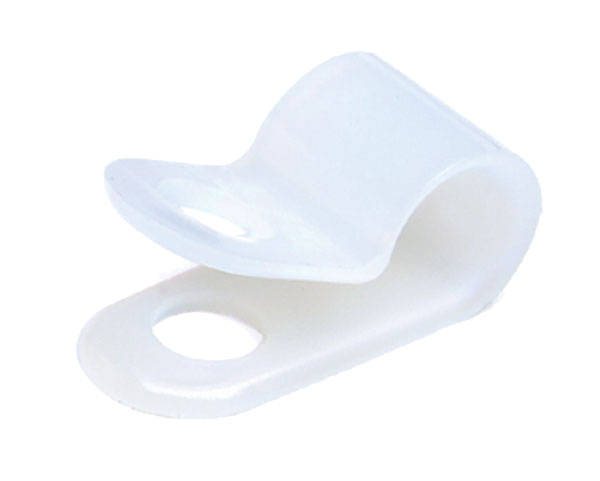
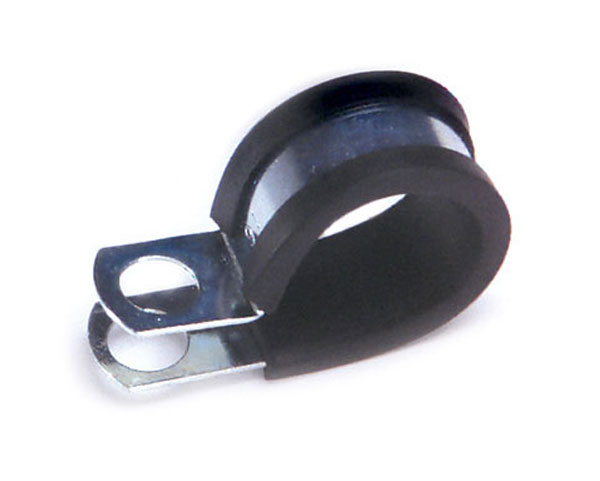
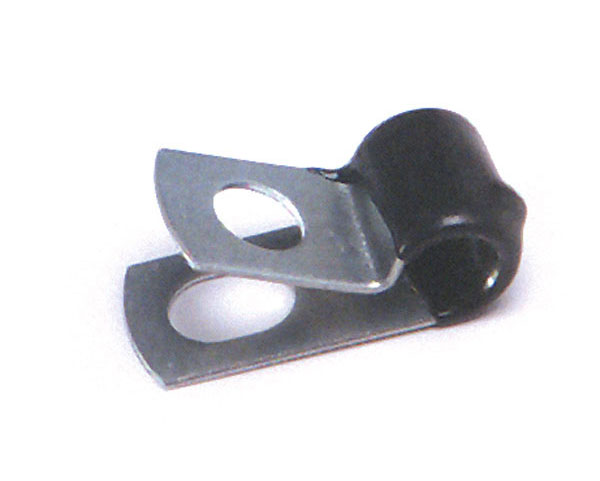



Wire clamps (above) come in a variety of materials and are important for securing wires.
AN INSTALLATION & ROUTING CHECKLIST
There are certain factors that should be considered virtually every time an installation or repair is done. The installation process should be done in such a way as to minimize the possible harmful effects to the wiring components and the vehicle itself.
GENERAL FACTORS:
CONDITIONS TO AVOID
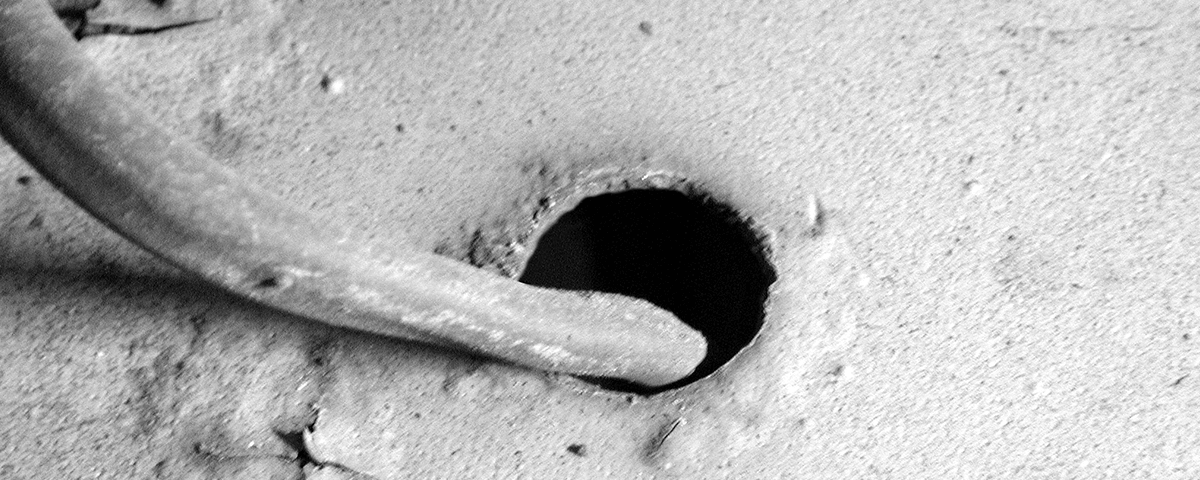

Avoid situations where wiring is in contact with sharp edges or abrasive surfaces.
SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR AVOIDING WATER PROBLEMS
AVOID PROBLEMS WITH FLEXING
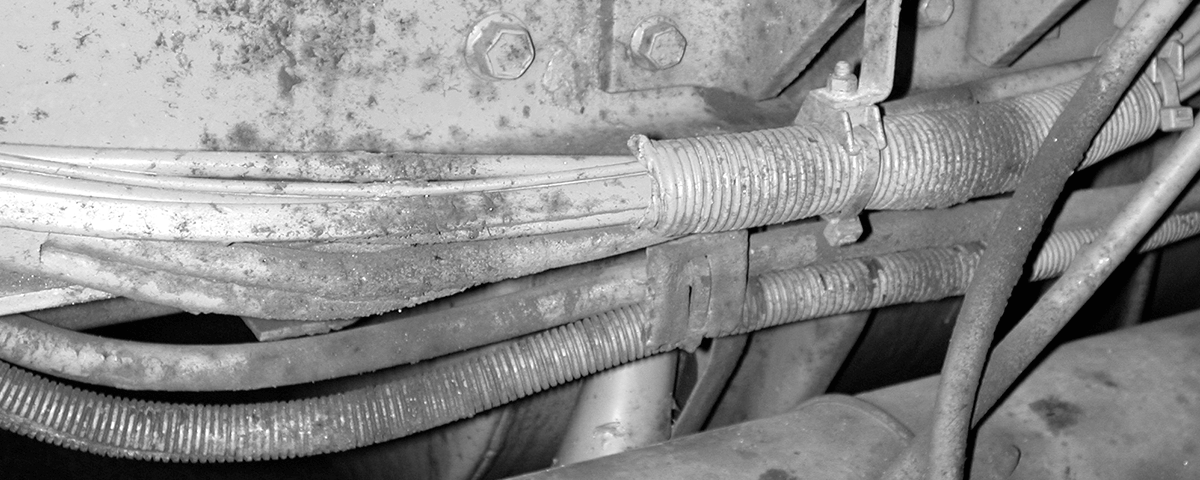
Secure wiring carefully to avoid the effects of vibration and road shock. This wiring has to live in a rough environment, but it’s well secured.
Use the self assessment below to gauge your understanding of this section. Place your answer in the box and then check your answer by clicking on the "show answer" link.
Or, you can skip the assessment.
Instructions:
Read the question.
Place your answer in the box.
Example:
True or False:
You should read the questions and then type your answer into the box.
show answer
True!
Begin:
1. True or False: Tape, especially electrical tape, is the correct product to use for securing wire bundles.
show answer
False
2. Heat shrink tubing shrinks as much as:
show answer
c) 4 to 1
3. Heat shrink tubing is used to protect connections from:
show answer
d) All of the above
4. True or False: When applying heat to a piece of shrink tube always start at the center to ensure that all moisture is forced out of the connection, working your way out to insure a proper seal
show answer
True
5. True or False: Dual-wall tubing is used in those areas that are unlikely to be subjected to moisture and corrosion.
show answer
False
6. True or False: Hot melt adhesive-style shrink tubing should be used where under hood temperatures are high and you need to form a barrier against corrosives, chemicals and moisture.
show answer
True
7. Convoluted tubing offers:
show answer
d) All of the above
8. True or False: Convoluted tubing is available in polypropylene, polyamide, PVC and cotton.
show answer
False
9. Tubing size should be selected so that the wire fills it to approximately ___ of its diameter:
show answer
d) 80%
10. Which of the following is not recommended for controlling and protecting wires and bundles?
show answer
d) PVC tape
11. Which of the following is not typically a benefit of securing wire along the designated path:
show answer
c) Some wires can be eliminated
12. True or False: The drawback to using nylon clamps is that they are prone to rust and corrosion.
show answer
False
13. The highest operating temperature for nylon clamps is:
show answer
d) 100° C
14. True or False: Some metal clamps are coated with neoprene rubber.
show answer
True
15. True or False: The term “mounting tie” refers to one that has an adhesive to affix it to a body or frame component.
show answer
False
16. Support points for wire bundles should be spread:
show answer
c) From 12 inches to 18 inches